Titanium is known as a transition metal on the periodic table of elements denoted by the symbol Ti. It is a lightweight, silver-gray material with an atomic number of 22 and an atomic weight of 47.90. It has a density of 4510 kg/m 3 , which is somewhere between the densities of aluminum and stainless steel. It has a melting point of roughly 3,032°F (1,667°C) and a boiling point of 5,948°F (3,287 C). It behaves chemically similar to zirconium and silicon. It has excellent corrosion resistance and a high strength to weight ratio.
 Titanium Application
Titanium Application
Titanium as a useful metal alloy was not commonly used. It is most often alloyed with molybdenum, manganese, iron, and aluminum. By weight titanium is one of the strongest readily available metals, making it ideal for wide range of practical applications. It is 45% lighter than steel with comparable strength, and twice as strong as aluminum while being only 60% heavier. Titanium is a metal present in meteorites and in the sun. It is also the ninth-most abundant metal in the crust of the Earth and occurs in the minerals rutile, ilmenite sphene, titanates and iron ores. In1946, William J. Kroll showed that titanium could be produced commercially.
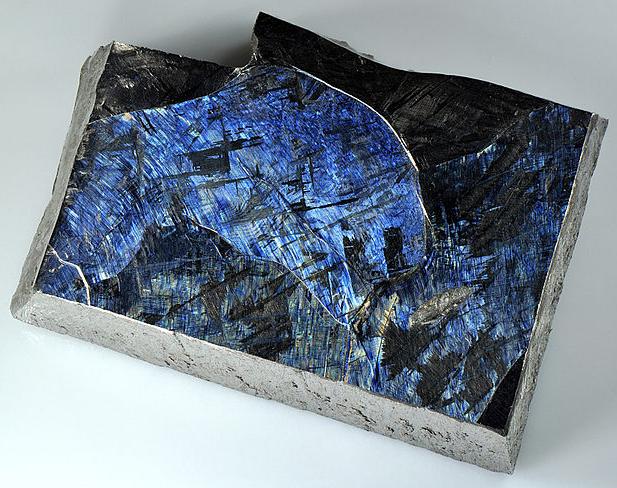 Titanium Metal
Titanium Metal
In commercial use, titanium alloys are used anywhere strength and weight are an issue. Bicycle frames, automobile and plane parts, and structural pieces are some common examples. In medical use titanium pins are used because of their non-reactive nature when contacting bone and flesh. Many surgical instruments, as well as body piercings are made of titanium for this reason as well.
You might also like
| Titanium and It’s Alloys Titanium Metal Titanium was... | Types of Materials Metals: Metals are elements... | Nickel and Nickel Alloys Nickel is a chemical element, with... | Semiconductor Materials A semiconductor is a substance,... |





 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope