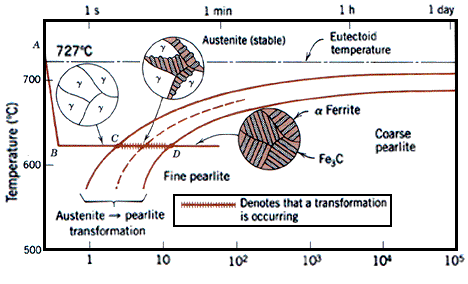
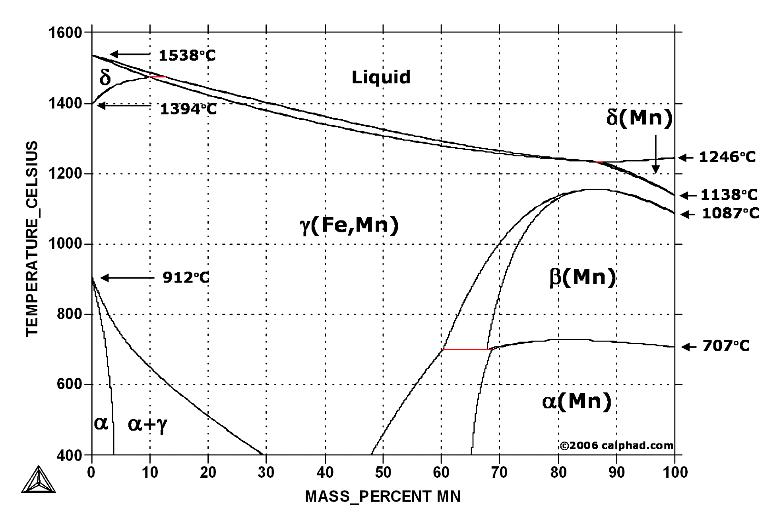
Austenite, also known as gamma phase iron is a metallic non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron, with an alloying element. In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1,000 K (1,340 °F); other alloys of steel have different eutectoid temperatures. It is named after Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen (1843–1902).
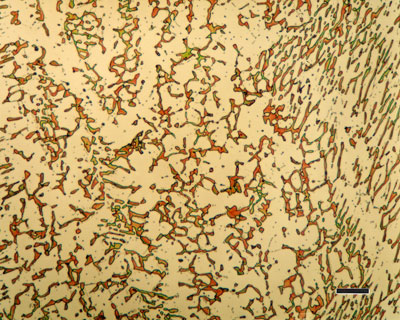
316 austenitic stainless steel, containing sigma phase. Source : https://www.paintertoolinc.com/
Austenite is a metallic, non-magnetic solid solution of carbon and iron that exists in steel above the critical temperature of 1333°F ( 723°C). Its face-centred cubic (FCC) structure allows it to hold a high proportion of carbon in solution. In many magnetic alloys, the Curie point, the temperature at which magnetic materials cease to behave magnetically, occurs at nearly the same temperature as the austenite transformation. This behavior is attributed to the paramagnetic nature of austenite, while both martensite and ferrite are strongly ferromagnetic.
You might also like
 Making pottery
Making pottery










 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope