The term “heat treating” for aluminum alloys is frequently restricted to the specific operations employed to increase strength and hardness of the precipitation-hardenable wrought and cast alloys. These usually are referred to as the “heat-treatable” alloys to distinguish them from those alloys in which no significant strengthening can be achieved by heating and cooling.
 Aluminum
Aluminum
Heat treatment to increase strength of aluminum alloys is a three-step process:
- Solution heat treatment : dissolution of soluble phases
- Quenching : development of supersaturation
- Age hardening : precipitation of solute atoms either at room temperature (natural aging) or elevated temperature (artificial aging or precipitation heat treatment).
Precipitation hardening, also called age hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys of aluminium, magnesium, nickel and titanium, and some stainless steels. It relies on changes in solid solubility with temperature to produce fine particles of an impurity phase, which impede the movement of dislocations, or defects in a crystal’s lattice.
You might also like
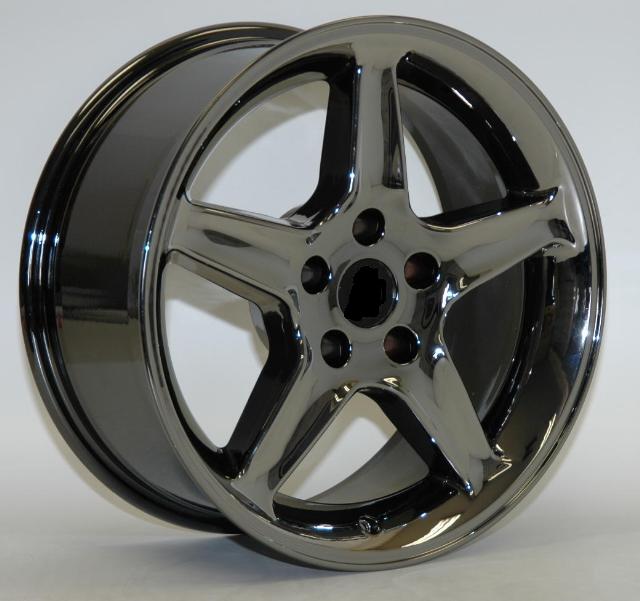
| Aluminum alloy Aluminum Alloy Wheel An alloy is a material... | Nitriding - How it works? Nitriding is a case hardening process... | Heat Treatment Furnaces Heat treating is a group of industrial and... | Forging A forge is a hearth used for forging.... |



 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope