Heat treating is a group of industrial and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass. Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve a desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering and quenching.
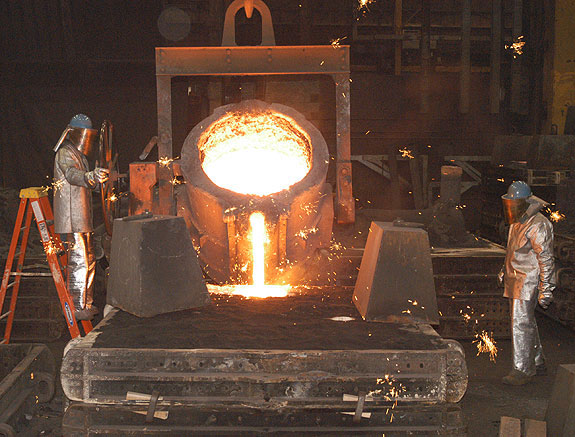
 Heat Treatment Furnace by Micron has installed a brand new (2006) heat treatment plant capable of soaking temperatures up to 1050ºC. Featuring fully programmable cycles, the fully automatic electric furnace improves metallurgical control and optimises mechanical properties due to supreme heat uniformity. The working envelope of 1200 x 1200 x 2000mm caters for loads of up to 2 Tonnes.
Heat Treatment Furnace by Micron has installed a brand new (2006) heat treatment plant capable of soaking temperatures up to 1050ºC. Featuring fully programmable cycles, the fully automatic electric furnace improves metallurgical control and optimises mechanical properties due to supreme heat uniformity. The working envelope of 1200 x 1200 x 2000mm caters for loads of up to 2 Tonnes.
It is noteworthy that while the termheat treatment applies only to processes where the heating and cooling are done for the specific purpose of altering properties intentionally, heating and cooling often occur incidentally during other manufacturing processes such as hot forming or welding. Heat treatment involves the use of heating or chilling, normally to extreme temperatures, to achieve a desired result such as hardening or softening of a material. Heat treatment techniques include annealing, case hardening, precipitation strengthening, tempering and quenching.
You might also like
| Heat Treatment of Steel Heat treating is a group of industrial... | What is Metallurgy ? Metallurgy is a domain of materials science... | Aluminum “Hardening” - How it works? The term “heat treating” for aluminum... | Foundry and Casting A foundry is a factory that produces... |



 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope