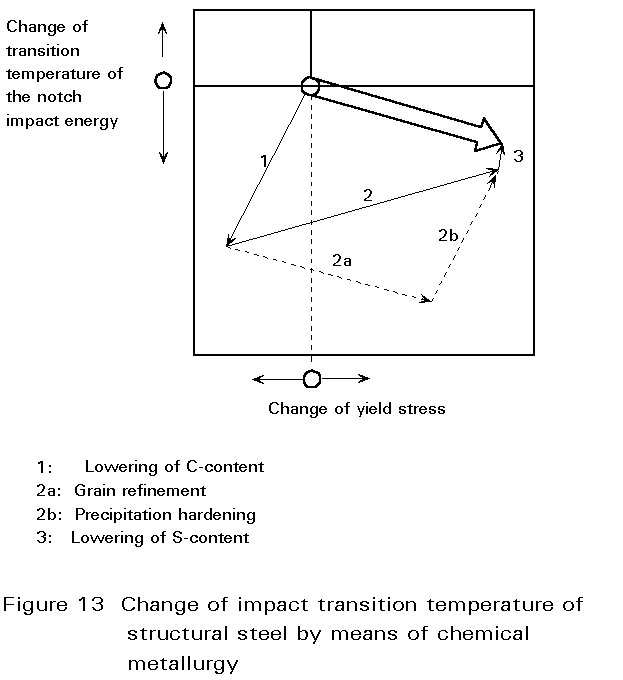
Precipitation Hardening Overview
Precipitation hardening also called age hardening, is a heat treatment technique used to increase the yield strength of malleable materials, including most structural alloys ofaluminium, magnesium, nickel, titanium, and some stainless steels. Precipitation hardening relies on changes in solid solubility with temperature to produce fine particles of an impurity phase, which impede the movement of dislocations, or defects in a crystal’s lattice. Unlike ordinary tempering, alloys must be kept at elevated temperature for hours to allow precipitation to take place. This time delay is called aging.
Note that two different heat treatments involving precipitates can alter the strength of a material: solution heat treating and precipitation heat treating. Solid solution strengtheninginvolves formation of a single-phase solid solution via quenching. Precipitation heat treating involves the addition of impurity particles to increase a material’s strength. Precipitation hardening via precipitation heat treatment is the main topic of discussion in this article.
You might also like
| Heat Treatment Furnaces Heat Treatment Furnaces of Steel Heat treating... | Optimal Combination of STRENGTH and TOUGHNESS Optimal Combination of STRENGTH and TOUGHNESS Preceding... | Aluminum “Hardening” - How it works? Heat Treatment of Aluminum The term “heat... | Do you know Heat Treatment process ? Heat Treatment Heat Treatment is the controlled... |

 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope