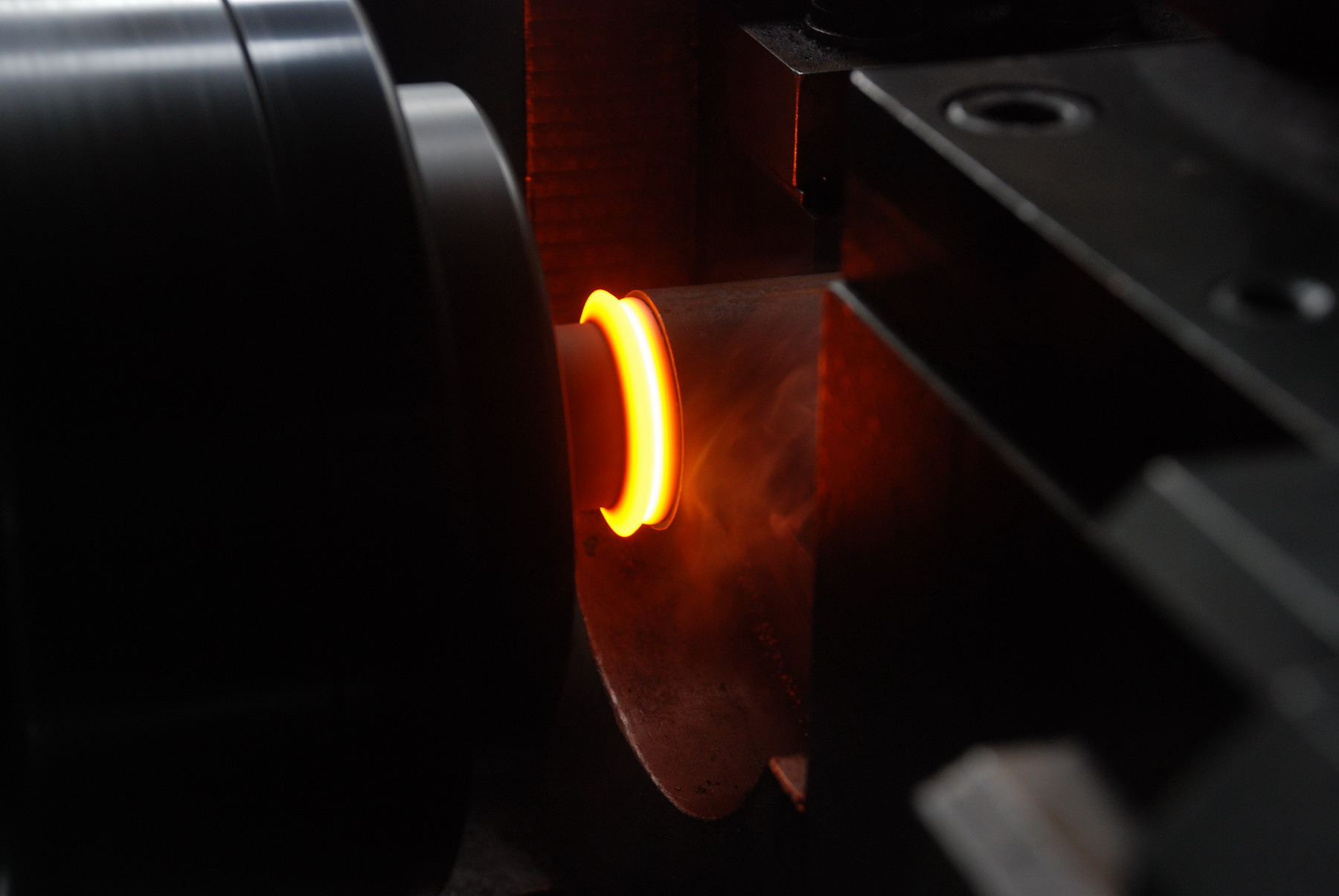
Spot Welding
Spot welding is a technique generally used to bond metals shaped into sheets no thicker than 3 millimeters. Unlike other welding techniques, spot welding can create precise bonds without generating excessive heating that can affect the properties of the rest of the sheet. This is achieved by delivering a large amount of energy in a short time in order to create controlled and reliable welds.
Robotic Spot Welding
Spot welding is a process in which contacting metal surfaces are joined by the heat obtained from resistance to electric current flow. Work-pieces are held together under pressure exerted by electrodes. Typically the sheets are in the 0.5 to 3 mm (0.020 to 0.12 in) thickness range. The process uses two shaped copper alloy electrodes to concentrate welding current into a small “spot” and to simultaneously clamp the sheets together. Forcing a large current through the spot will melt the metal and form the weld. The attractive feature of spot welding is a lot of energy can be delivered to the spot in a very short time (approximately ten milliseconds). That permits the welding to occur without excessive heating to the rest of the sheet.
You might also like
| Welding What is Welding ? Welding is a fabrication... | What is Plastic Welding ? Welding Plastic Definition Plastic welding... | How does Friction Welding Work ? What is Friction Welding ? Friction welding... | Welding Procedure What Are Welding Procedures ? A Welding... |

 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope