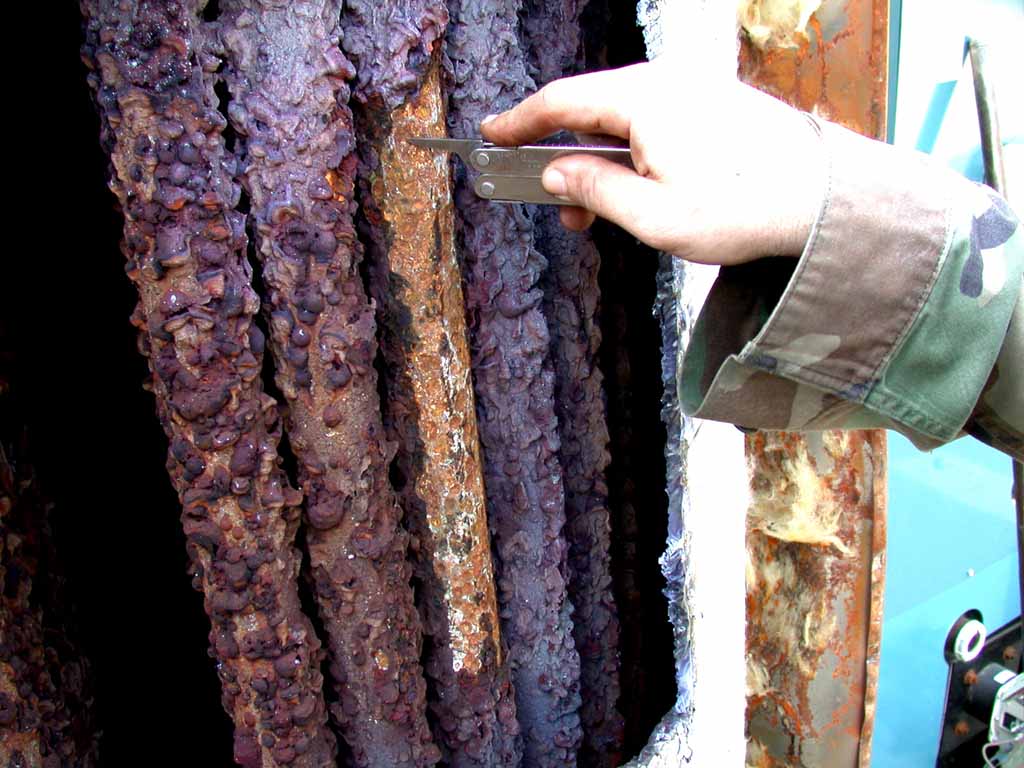
Corrosion
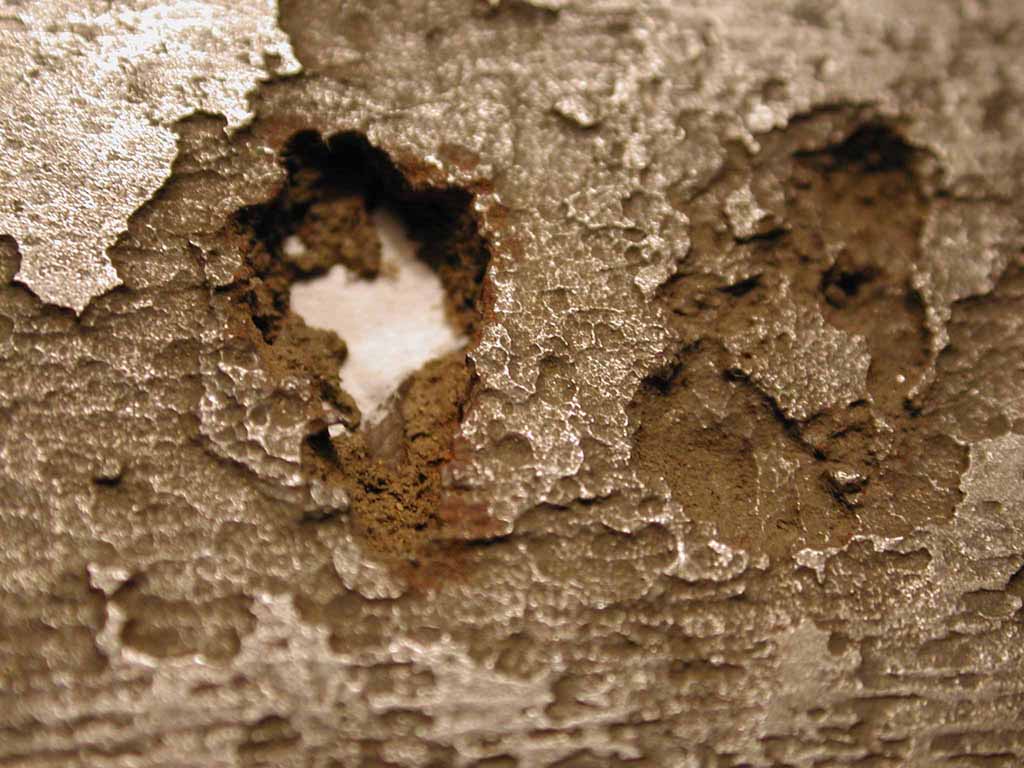
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen.
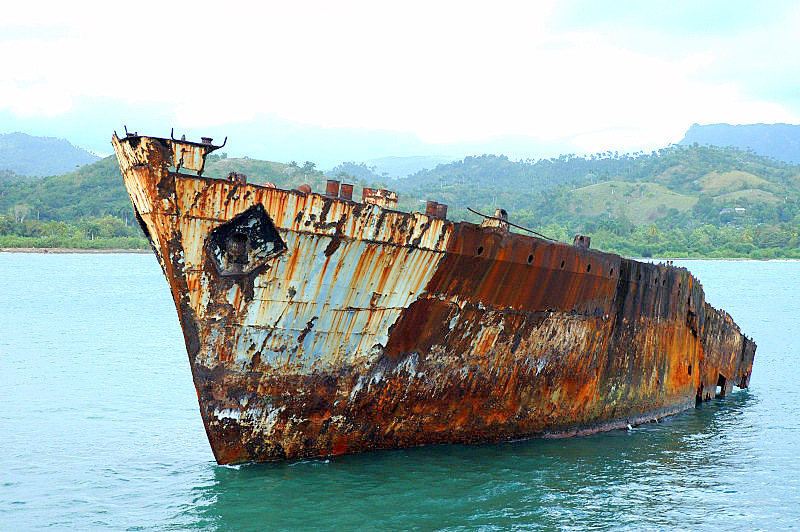
Formation of an oxide of iron due to oxidation of the iron atoms in solid solution is a well-known example of electrochemical corrosion, commonly known as rusting. This type of damage typically produces oxide(s) and/or salt(s) of the original metal. Corrosion can also occur in materials other than metals, such as ceramics or polymers, although in this context, the term degradation is more common.
Corrosion is the primary means by which metals deteriorate. Most metals corrode on contact with water (and moisture in the air), acids, bases, salts, oils, aggressive metal polishes, and other solid and liquid chemicals. Metals will also corrode when exposed to gaseous materials like acid vapors, formaldehyde gas, ammonia gas, and sulfur containing gases. Corrosion specifically refers to any process involving the deterioration or degradation of metal components. The best known case is that of the rusting of steel. Corrosion processes are usually electrochemical in nature, having the essential features of a battery.
You might also like
| The Casting Process Pictures Metallurgy Casting Process These are the... | Corrosion What is Corrosion ? Corrosion is the disintegration... | Welding Pictures Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that... | Corrosion in Water Water Corrosion Corrosion is a chemical... |




 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope