What is Stress Relieving?
Stress Relieving - A definition
Stress Relieving consists of heating the steel to a temperature below the critical range to relieve the stresses resulting from cold working, shearing, or gas cutting. It is not intended to alter the microstructure or mechanical properties significantly.also a process for making material softer.
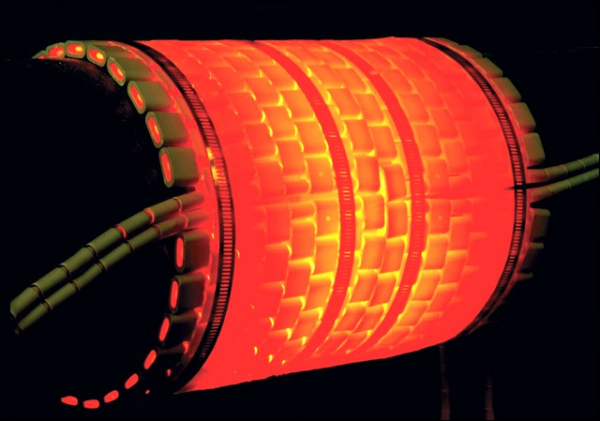 Stress relief and post weld heat treatment
Stress relief and post weld heat treatment
However stress relieving does not change the material properties as does annealing and normalizing. A material can be stress relieved by heating it to a specific temperature that is lower than that of annealing or normalizing and letting it cool to room temperature inside or outside of the oven. This heat treatment is typically used on parts that have been severely stressed during fabrication.
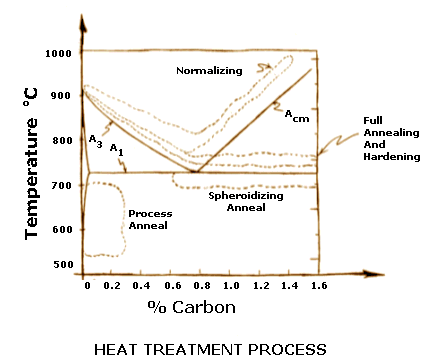
Stress relieving is done by subjecting the parts to a temperature of about 75 ºC (165 ºF) below the transformation temperature,line A1 on the diagram, which is about 727 ºC (1340 ºF) of steel—thus stress relieving is done at about 650 ºC (1202 ºF) for about one hour or till the whole part reaches the temperature. This removes more than 90% of the internal stresses. Alloy steels are stress relieved at higher temperatures. After removing from the furnace, the parts are air cooled in still air.
As the name implies, the purpose of this process is to remove internal residual stresses from steels. The stresses may have come from the steel making mills, machining, forming, welding etc.
If residual stresses are not removed prior to hardening, distortion may occur, whilst if stresses are left in components before they go into service, then premature failures can result, as well as more subtle movement causing the parts to go out of tolerance.
To Stress relieve steels, heat the parts to a temperature of about 650ºC for a minimum of one hour or till the whole part reaches the temperature. This will remove most of the internal stresses. After removing from the furnace, they are air cooled in still air.
Typical parts that benefit from stress relieving are large and complex welded assemblies, castings with a lot of machining, parts with tight dimensional tolerances and machined parts that have had a lot of stock removal or rapid stock removal.
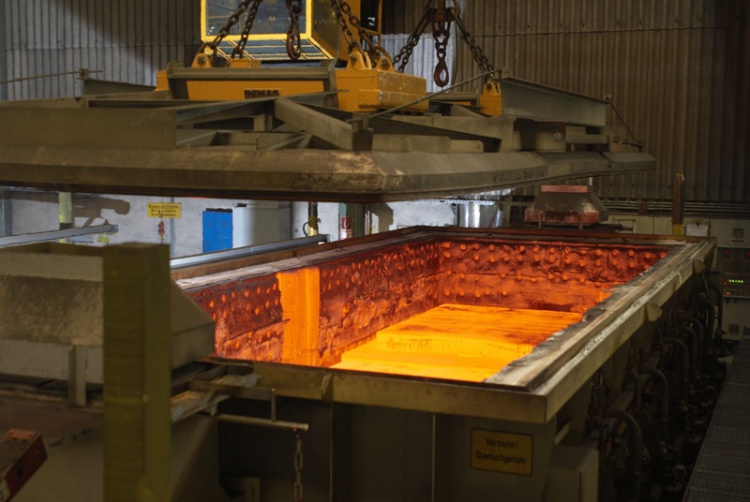 Stress Relieving Furnace
Stress Relieving Furnace
It is worth noting that many heat treatments and welding processes cause stresses in the material that can lead to warpage either after the heat treating process or during subsequent machining operations. Of specific concern is the stress induced by welding. If a weldment is to be machined it should almost always be stress relieved or normalized before the machining process. This is because machining chunks of material from a stressed weldment redistributes the internal stresses and can cause the part to warp. If the stresses are first relaxed then abrupt changes in geometry after machining are reduced.
Machining induces stresses in parts. The bigger and more complex the part, the more the stresses. These stresses can cause distortions in the part long term. If the parts are clamped in service, then cracking could occur. Also hole locations can change causing them to go out of tolerance. For these reasons, stress relieving is often necessary.
Typically, the parts that benefit from stress relieving are large and complex weldments, castings with a lot of machining, parts with tight dimensional tolerances and machined parts that have had a lot of stock removal performed.





 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers  Aluminum
Aluminum  Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions  Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze  Nickel
Nickel  Magnets
Magnets  Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel  Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing  Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers  Titanium
Titanium  Tungsten
Tungsten  Wire Rope
Wire Rope