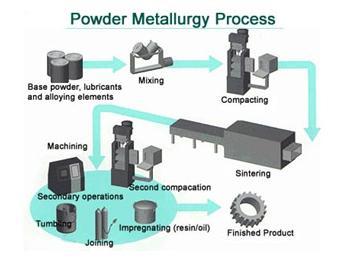
 Powder Metallurgy Process, source : https://www.themetalcasting.com/
Powder Metallurgy Process, source : https://www.themetalcasting.com/
Powder metallurgy is a forming and fabrication technique consisting of three major processing stages. First, the primary material is physically powdered, divided into many small individual particles. Next, the powder is injected into a mold or passed through a die to produce a weakly cohesive structure (via cold welding) very near the dimensions of the object ultimately to be manufactured.
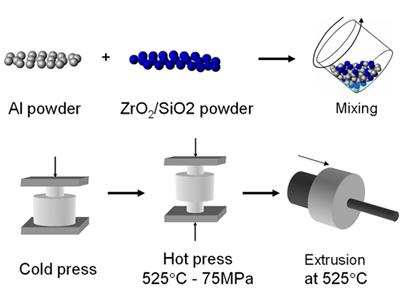 Powder metallurgy route.Source : https://www.weck.ca/
Powder metallurgy route.Source : https://www.weck.ca/
Pressures of 10-50 tons per square inch are commonly used. Also, to attain the same compression ratio across more complex pieces, it is often necessary to use lower punches as well as an upper punch. Finally, the end part is formed by applying pressure, high temperature, long setting times (during which self-welding occurs), or any combination thereof.
 Ball by Powder Metallurgy Procesing, source : https://www.stellite.de/
Ball by Powder Metallurgy Procesing, source : https://www.stellite.de/
 Diesel Engine Bush -Powder Metallurgy Products
Diesel Engine Bush -Powder Metallurgy Products
Two main techniques used to form and consolidate the powder are sintering and metal injection molding. Recent developments have made it possible to use rapid manufacturing techniques which use the metal powder for the products. Because with this technique the powder is melted and not sintered, better mechanical strength can be accomplished.
 Powder Metallurgy Cycle. Source : EPMA
Powder Metallurgy Cycle. Source : EPMA
The history of powder metallurgy and the art of metals and ceramics sintering are intimately related. Sintering involves the production of a hard solid metal or ceramic piece from a starting powder. There is evidence that iron (Fe) powders were fused into hard objects as early as 1200 B.C. In these early manufacturing operations, iron was extracted by hand from metal sponge following reduction and was then reintroduced as a powder for final melting or sintering.
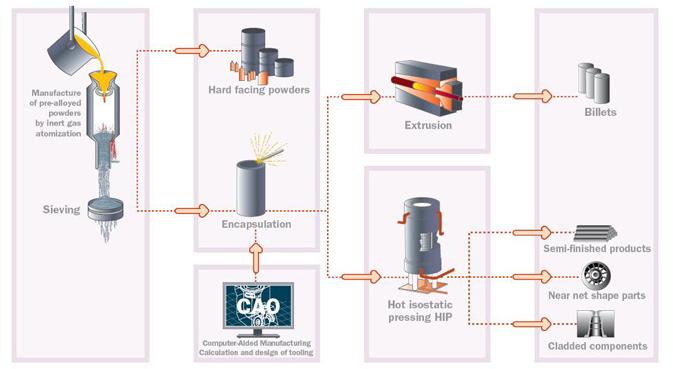 Modern Powder Metallurgy Processing. The Aubert & Duval technology is used to melt steels with properties that are unachievable through traditional metallurgical methods. Source : https://www.aubertduval.com
Modern Powder Metallurgy Processing. The Aubert & Duval technology is used to melt steels with properties that are unachievable through traditional metallurgical methods. Source : https://www.aubertduval.com
 The three primary steps in powder metallurgy. Source : https://www.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/
The three primary steps in powder metallurgy. Source : https://www.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/
Powder Consolidation
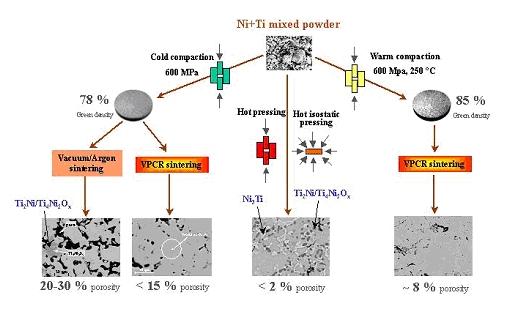 Powder metallurgical processings NiTi alloys, source : https://nitig.ch/9054.html
Powder metallurgical processings NiTi alloys, source : https://nitig.ch/9054.html
Cold Isostatic Pressing
Isostatic powder compacting is a mass-conserving shaping process. Fine metal particles are placed into a flexible mold and then high gas or fluid pressure is applied to the mold. The resulting article is then sintered in a furnace. This increases the strength of the part by bonding the metal particles. This manufacturing process produces very little scrap metal and can be used to make many different shapes.
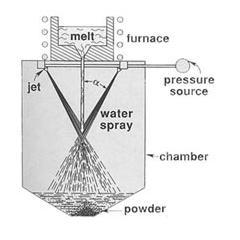 Water Atomization Process: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
Water Atomization Process: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
 Vertical Gas Atomizer: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
Vertical Gas Atomizer: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
Hot Isostatic Pressing
 Centrifugal Atomization by the Rotating Electrode Process: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
Centrifugal Atomization by the Rotating Electrode Process: Source “Powder Metallurgy Science” Second Edition, R.M. German, MPIF.
 Metal Powder Injection Modeling (M. I. M.) Product.
Metal Powder Injection Modeling (M. I. M.) Product.
Hot Forging (Powder Forging)
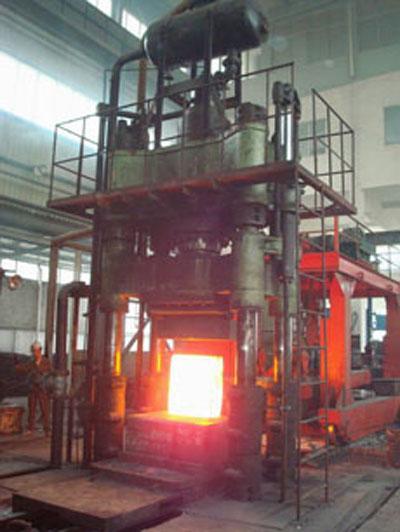 Hot Forging Hydraulic Press
Hot Forging Hydraulic Press
Sintering
Sintering is the process whereby powder compacts are heated so that adjacent particles fuse together, thus resulting in a solid article with improved mechanical strength compared to the powder compact. This “fusing” of particles results in an increase in the density of the part and hence the process is sometimes called densification. There are some processes such as hot isostatic pressing which combine the compaction and sintering processes into a single step.
 Sintering Process
Sintering Process
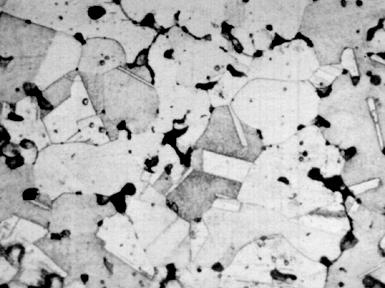 Microstructure of Sintered Bronze (Magnification: 200X), source : https://www.copper.org/
Microstructure of Sintered Bronze (Magnification: 200X), source : https://www.copper.org/
Metal Injection Moulding (MIM)
 Schematic of the metal injection molding process, source : https://nitig.ch/
Schematic of the metal injection molding process, source : https://nitig.ch/
You might also like
| Metal Spraying Metal spraying is spraying hot metal... | Phase Diagrams Fe-Mn, Fe-Co, Fe-Mo In pure iron, the A4 (1394 °C) and... | Metallurgy Glossary Metallurgy Glossary Activity: A function... | The Casting Process Pictures These are the metallurgy pictures jobs and... |


 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope