Cold Working of Metals
Cold working is the plastic deformation shaping process of metals which is performed below recrystallization temperature. Usually, recrystallization temperature is 40% of melting point temperature (TR=0.40xTM). Advantages are; no oxides on the surface after operation, no hydrogen embrittlement, lower costs for process and equipment, hardening from strain. Disadvantages are; stress in the body therefore mostly it needs recovery process, much more load power necessity for plastic deformation, it becomes brittle depends to cold working percentage.
Cold working is the plastic deformation of metals below the recrystallization temperature. In most cases, such cold forming is done at room temperature. The major cold-working operations can be classified basically as squeezing, bending, shearing and drawing.
Altering the shape or size of a metal by plastic deformation. Processes include rolling, drawing, pressing, spinning, extruding and heading, it is carried out below the recrystallisation point usually at room temperature. Hardness and tensile strength are increased with the degree of cold work whilst ductility and impact values are lowered. The cold rolling and cold drawing of steel significantly improves surface finish.
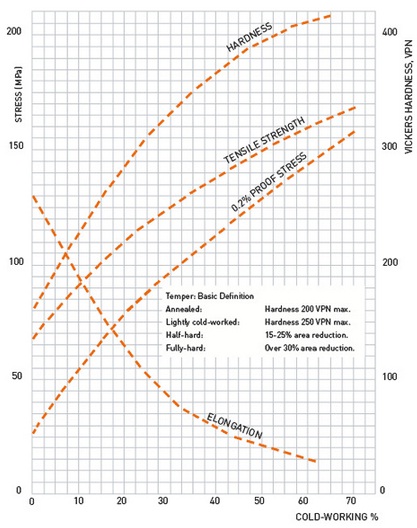 Effect of cold working on the mechanical properties of an austenitic stainless steel
Effect of cold working on the mechanical properties of an austenitic stainless steel
Cold working is the plastic deformation of metals below the recrystallization temperature. In most cases of manufacturing, such cold forming is done at room temperature. Sometimes, however, the working may be done at elevated temperatures that will provide increased ductility and reduced strength, but will be below the recrystallization temperature.
When compared to hot working, cold-working processes have certain distinct advantages :
- No heating required
- Better surface finish obtained
- Superior dimension control
- Better reproducibility and interchangeability of parts
- Improved strength properties
- Directional properties can be minimized
Some disadvantages associated with cold-working processes include :
- Higher forces required for deformation
- Heavier and more powerful equipment required
- Less ductility available
- Metal surfaces must be clean and scale-free
- Strain hardening occurs (may require intermediate anneals)
- Imparted directional properties may be detrimental
- May produce undesirable residual stresses
Squeezing Processes
Most of the cold-working squeezing processes have identical hot-working counterparts or are extensions of them. The primary reasons for deforming cold rather than hot are to obtain better dimensional accuracy and surface finish. In many cases, the equipment is basically the same, except that it must be more powerful.
Cold Rolling
Cold rolling accounts for by far the greatest tonnage of cold-worked products. Sheets, strip, bars and rods are cold rolled to obtain products that have smooth surfaces and accurate dimensions.
Swaging
Swaging basically is a process for reducing the diameter, tapering, or pointing round bars or tubes by external hammering. A useful extension of the process involves the formation of internal cavities. A shaped mandrel is inserted inside a tube and the tube is than collapsed around it by swaging.
Cold Forging
Extremely large quantities of products are made by cold forging, in which the metal is squeezed into a dive cavity that imparts the desired shape. Cold heading is used for making enlarged sections on the ends of rod or wire, such as the heads on bolts, nails, rivets and other fasteners.
Sizing
Sizing involves squeezing areas of forgings or ductile castings to a desired thickness. It is used principally on basses and flats, with only enough deformation to bring the region to a desired dimension.
You might also like
| What is Annealing Heat Treatment ? Annealing of Steel Heat Treatment Annealing... | What is Metal Extrusion ? Metal Extrusion Extrusion is the process... | Cold Metal Spraying How Does Cold Spray Work ? In the 1990s,... | Do you know Heat Treatment process ? Heat Treatment Heat Treatment is the controlled... |
 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope