Oxy-fuel welding - a Definition
Gas Welding or Oxy-fuel welding are processes that use fuel gases and oxygen to weld and cut metals, respectively. French engineers Edmond Fouché and Charles Picard became the first to develop oxygen-acetylene welding.
Pure oxygen, instead of air (20% oxygen/80% nitrogen), is used to increase the flame temperature to allow localized melting of the workpiece material (e.g. steel) in a room environment.
A common propane/air flame burns at about 3,630 °F (2,000 °C), a propane/oxygen flame burns at about 4,530 °F (2,500 °C), and an acetylene/oxygen flame burns at about 6,330 °F (3,500 °C).
Oxy-fuel is one of the oldest welding processes, though in recent years it has become less popular in industrial applications. However, it is still widely used for welding pipes and tubes, as well as repair work.
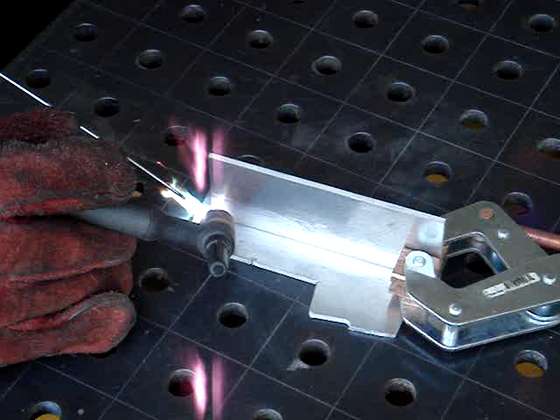
It is also frequently well-suited, and favored, for fabricating some types of metal-based artwork. In oxy-fuel welding, a welding torch is used to weld metals.
Welding metal results when two pieces are heated to a temperature that produces a shared pool of molten metal. The molten pool is generally supplied with additional metal called filler. Filler material depends upon the metals to be welded.
You might also like
| Welding Procedure What Are Welding Procedures ? A Welding... | Welding Positions What`s Kind of Welding Positions ? Welding... | What is TIG WELDING ? TIG Welding - an Overview Gas tungsten arc... | Arc Welding Welding Arc Overview Arc welding is the... |

 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope