Metal Alloys - A Definition
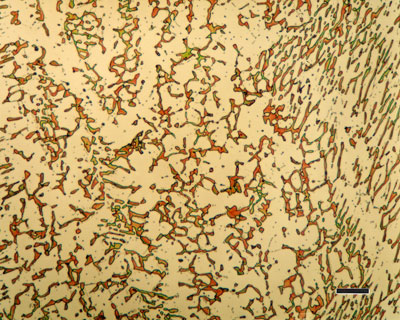
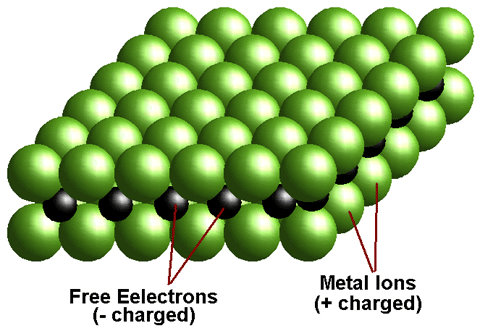
Metal alloy is a homogeneous mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal (heat treatment) history. Alloys usually have different properties from those of the component elements.
 Bullet from Lead Metal Alloy
Bullet from Lead Metal Alloy
Alloying a metal is done by combining it with one or more other metals or non-metals that often enhance its properties. For example, steel is stronger than iron, its primary element. The physical properties, such as density, reactivity, Young’s modulus, and electrical and thermal conductivity, of an alloy may not differ greatly from those of its elements, but engineering properties such as tensile strength and shear strength may be substantially different from those of the constituent materials. This is sometimes a result of the sizes of the atoms in the alloy, because larger atoms exert a compressive force on neighboring atoms, and smaller atoms exert a tensile force on their neighbors, helping the alloy resist deformation.
You might also like
| Metallurgy Glossary What is Metallurgy ? Metallurgy is a domain... | Austenite - Gamma Iron Austenite - a Definition Austenite also... | Properties of Metal Metal Properties - Overview A metal is a... | What is Superalloy ? What is Superalloy ? - Definition and Meaning A... |
 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers
 Aluminum
Aluminum
 Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions
 Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze
 Nickel
Nickel
 Magnets
Magnets
 Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
 Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing
 Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers
 Titanium
Titanium
 Tungsten
Tungsten
 Wire Rope
Wire Rope